As technology continues to evolve, the need for top-tier cyber security implementations will be essential to protect against the hundreds of cyber attacks targeted against businesses each year. That is why it’s unsurprising to see how nearly 66% of cybersecurity companies expect their spending to be driven by security compliance mandates within the coming years.
Nearly 44% of firms report how they asked for proof of cyber security as part of their RFP (request for proposal process). This article will discuss what it means for an organization to comply with cybersecurity practices, its benefits, and the top security compliance standards and regulations that businesses should comply with.
Table of Contents
What Is Cyber Security Compliance?
Cybersecurity compliance refers to the set of rules and regulations that organizations must follow to protect their digital assets from cyber threats. These rules and regulations are designed to ensure that organizations take the necessary steps to safeguard their data and systems from unauthorized access, theft, and other malicious activities. Cybersecurity compliance is essential for businesses of all sizes as cyber threats continue to grow in frequency and complexity.
The Importance Of Cyber Security Compliance
According to a report by Cisco, nearly 50% of all large enterprises have spent $1 million annually on cybersecurity implementations. Many organizations have realized that maintaining compliance and governance over confidential, accurate, and available systems is essential to combat cybercrime. CEOs and CFOs can help protect their organizations’ reputations and financial stability by prioritizing cybersecurity.
Additionally, cybersecurity compliance can help protect business customers. It can also prevent your company from incurring significant financial costs due to a breach or bankruptcy. Consistent data usage can improve operational efficiency and support your business’s success.
The Top Ten Types of Cyber Security Compliance Regulations
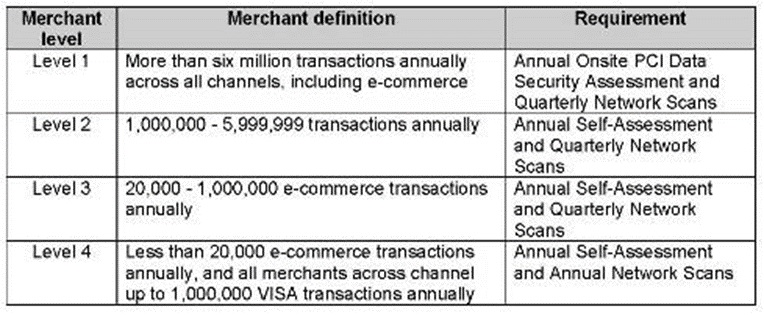
PCI-DSS
PCI DSS is a set of security standards designed to ensure that all companies that accept, process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment.
The Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) developed the standard, founded by major credit card companies such as Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover, and JCB.
The Top Configurations That Companies Should Implement To Be PCI-DSS Compliant include:
-Configuring a firewall that allows and blocks network traffic to and from certain systems.
-Implementing a proper network segmentation to isolate cardholder data on their private network away from other networks.
-The encryption of all data that contains sensitive credit card information both in transit and at rest. Only the most secure encryption algorithms, such as AES and RSA, should be used to encrypt this information.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
The HIPPA regulation applies to healthcare organizations and protects individuals’ health information. This regulation is crucial for safeguarding sensitive patient data and ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of health records.
The healthcare information protected by this regulation includes diagnoses, treatment information, medical test results, and prescription information. Businesses such as hospitals can pay a high price for not complying with HIPAA standards. This includes penalty fines between $100 to $50,000 per violation.
HIPAA compliance includes strict guidelines on implementing access controls, encryption, and audit trails to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI).
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR is a European Union regulation that protects EU citizens’ privacy and personal data.
Organizations handling EU citizens’ data must adhere to principles such as asking for consent to collect users’ data, data minimization or collecting the least amount of user data as possible, and the right for users to ask that their data be erased from a company’s system. GDPR has global implications, as companies outside the EU that handle EU citizens’ data must also comply.
Overall, the regulation emphasizes transparency, accountability, and the implementation of appropriate security measures.
FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act) and the Risk Management Framework (RMF)
The FISMA regulation governs information security for federal agencies in the United States, emphasizing risk management. FISMA requires federal agencies to develop, implement, and maintain information security programs.
The Risk Management Framework (RMF) is a key component of FISMA’s standards, guiding agencies in managing and mitigating cybersecurity risks.
GLBA (Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act)
GLBA, or the Gramm-Leah-Biley Act, pertains to the protection of consumer financial information and applies to financial institutions. GLBA mandates financial institutions like banks and credit unions to establish information security programs to protect the confidentiality and integrity of nonpublic personal information (NPI).
GLBA-protected information includes bank account numbers, credit history, income, and transaction history.
SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act)
SOX, or the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, enforces financial reporting and disclosure requirements with a focus on preventing corporate fraud. SOX compliance is essential for publicly traded companies, requiring strict controls over financial reporting processes.
The regulation addresses data accuracy, accountability, and transparency issues in financial disclosures. SOX aims to restore investor confidence by holding companies accountable for the accuracy and reliability of their financial statements.
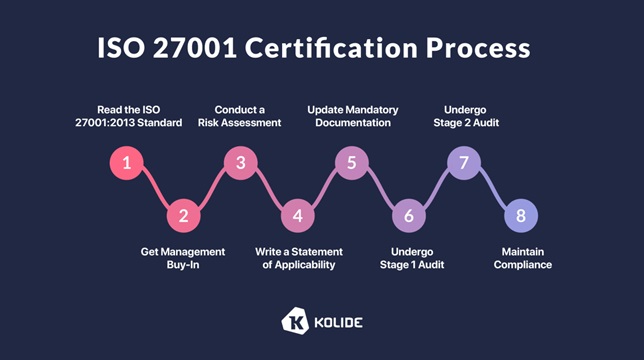
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is an international standard for information security management systems, providing a framework for organizations to establish and maintain an effective information security management system.
This widely recognized regulation focuses on risk management, continuous improvement, and a systematic approach to information security. Compliance demonstrates an organization’s commitment to protecting information assets and provides a structured methodology for identifying and managing security risks.
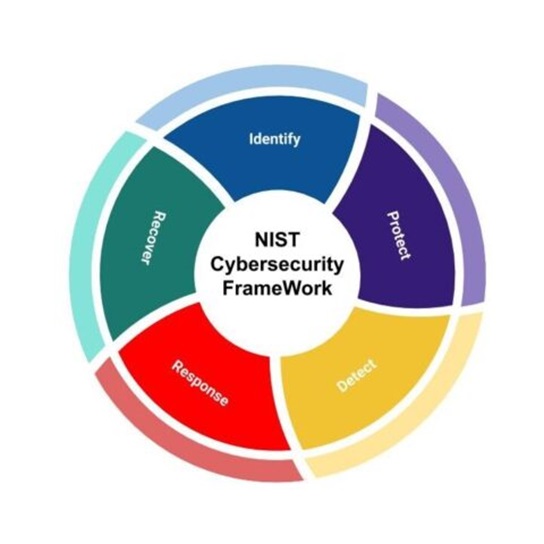
NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), it provides a voluntary framework for improving cybersecurity risk management. The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is a comprehensive set of guidelines, standards, and best practices designed to enhance an organization’s cybersecurity posture.
It consists of five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Organizations can use the framework to assess and strengthen their cybersecurity capabilities, aligning with industry best practices.
CIS Controls (Center For Internet Security Controls)
CIS Controls or Centr For Internet Security Controls is a set of best practices designed to help organizations assess and improve their cybersecurity posture. The CIS Controls, developed by the Center for Internet Security, offer a prioritized set of actions to enhance cybersecurity resilience.
These controls cover various aspects, including asset management, continuous vulnerability assessment, and data protection. Implementing the CIS Controls provides organizations with a structured approach to mitigating cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
NERC CIP (North American Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection)
The NERP CIP, or North America Electric Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection, focuses on the cybersecurity of the North American power grid and associated systems. NERC CIP establishes standards to secure critical infrastructure in the electric power industry. The regulations cover areas such as access controls, incident response, and security monitoring to ensure the reliability and resilience of the power grid. Compliance is crucial for safeguarding against cyber threats that could impact the availability of electrical power.
How Do Organizations Officially Get Cyber Security Compliance Certified?
Consult With Legal and Compliance Experts
After deciding what specific regulations, industry standards, and frameworks apply to your organization, businesses should look to work with legal and compliance experts in the cybersecurity field to determine the requirements of the regulations they are trying to abide by. These professionals can also assist in interpreting legal language and guide the organization in establishing compliance practices.
Conduct a Gap Analysis
Businesses can then conduct a comprehensive gap analysis with legal and compliance experts. This involves assessing the organization’s current cybersecurity practices against relevant regulations and standards requirements. Areas where improvements are needed can be identified.
Develop a Compliance Roadmap
Based on the gap analysis, a compliance roadmap can be created that outlines the specific steps the organization needs to take to address identified gaps. This roadmap should include timelines, responsibilities, and milestones.
Engage with Certification Bodies (If Applicable)
If seeking certification is part of the compliance strategy, organization leaders can engage with recognized certification bodies that specialize in cybersecurity. Examples include certification bodies for ISO 27001, SOC 2, or other industry-specific certifications.
Prepare for Certification Assessments
Organization leaders can work closely with the certification body to prepare for upcoming assessments. This may involve providing documentation, facilitating on-site visits, and demonstrating how the organization meets the requirements of the chosen certification through penetration testing, vulnerability scans, or general system audits.
Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes
It is important to monitor changes in relevant regulations and standards regularly. Businesses should stay informed about updates to compliance requirements and adjust organizational practices accordingly.
Employee Training and Awareness
Ensure that employees are trained and aware of their roles in maintaining cybersecurity compliance. This includes understanding policies, reporting incidents, and participating in ongoing training programs.
Benefits of Cybersecurity Compliance
Identify, Prepare For, and Prevent Data Breaches
Benefit: Enhanced Cyber Resilience
By being in cybersecurity compliance, companies can proactively identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their systems through regular assessments and audits.
This heightened awareness allows organizations to effectively prepare for and implement measures to prevent data breaches.
Compliance mandates often include specific requirements for incident response planning, ensuring that companies are well-prepared to detect, respond to, and recover from cybersecurity incidents.
This reduces the likelihood of data breaches and minimizes the impact when incidents occur, contributing to enhanced overall cyber resilience.
Maintain Company Trust and Protect Brand Awareness
Benefit: Preserving Reputation and Customer Trust
Cybersecurity compliance is closely linked to the protection of sensitive customer data. By adhering to regulations and implementing robust security measures, companies signal their commitment to safeguarding customer information.
This commitment, in turn, fosters trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders. Maintaining trust is crucial for preserving the company’s reputation and brand awareness.
In the event of a data breach, complying demonstrates that the organization took reasonable steps to protect data, mitigating potential damage to its reputation. A trusted and reputable brand will likely retain customer loyalty and attract new business opportunities.
Improve Data Access Controls and Managing Data
Benefit: Enhanced Data Governance and Compliance Adherence
Cybersecurity compliance frameworks often emphasize the importance of effective data access controls and data management practices. By aligning with these requirements, companies improve their overall data governance.
This involves defining and implementing policies and procedures for managing data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to destruction. Improved data access controls ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Enhanced data governance helps organizations comply with regulations and improves operational efficiency, data quality, and strategic decision-making processes.
Employee Awareness and Training
Benefit: Cybersecurity compliance often involves employee training programs to enhance awareness of security best practices. Educated employees are more likely to recognize and avoid security threats, reducing the risk of social engineering attacks and internal security breaches.
Conclusion
As businesses continue to navigate the evolving cybersecurity landscape, prioritizing compliance fortifies defenses against cyber threats and preserves trust, brand reputation, and financial stability in an increasingly digitized world. Organizations and their employees should stay diligent in educating themselves with the latest security regulations and rules so that their daily operations can remain safe from attacks and in compliance with industry standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Often Is an Organization’s Cyber Security Compliance Tested For?
This answer is different for each cyber security compliance standard that is being tested for, whether that be PCI-DSS, HIPPA, SOX, etc. For instance, PCI-DSS tests should typically be done every quarter.
How Much Do Cyber Security Compliance Tests Cost, and Who Are They Conducted By?
Cyber Security Compliance tests and audits typically range from $700 to $2500.
They are usually conducted by qualified penetration testers certified in the compliance standard they are testing for, such as PCI-DSS. These penetration testers can be employees within the testing company’s organization or by a third-party company.
What are the Financial Penalties Of Not Being In Cyber Security Compliance?
Companies can pay hefty fines for not complying with cyber security best practices. For instance, businesses not complying with the GDPR can face fines of up to $20 million or 4% of the company’s annual global turnover.