Two decades ago, any company with an IT infrastructure meant they were setting up servers in a room. The company would also have a highly paid large infrastructure team who would be constantly trying to keep up the set-up and cater to ever-changing demands.
Any upgrade of resources like network, security, databases or storage etc. meant purchasing new hardware and software. Time and effort to implement this change would be so huge that many companies would only do the bare essentials. Cloud computing changed all that.
What is Cloud Computing and Cloud Management Software?
Cloud computing is a technology that delivers various computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, artificial intelligence, and more over the internet or “the cloud.” The main goal of cloud computing is to give businesses and individuals the ability to store and process their data in third-party data centers.
Cloud Management Software is a set of tools and technologies used for monitoring and operating services, applications, and data in the cloud. It’s designed to maintain efficient use of resources in a cloud computing environment and can work across several types of cloud models, including hybrid, public, and private.
The main functions of cloud management software include automating processes, orchestrating tasks, providing visibility into the cloud environment, and ensuring cloud security. These platforms often provide features like resource inventory, metering and billing, workload optimization, access controls, and capacity planning.
Cloud management software allows a secure way to lease resources on-demand and has a pay-as-you-go model. This has created a completely new way of handling the IT infrastructure needs of any company.
A startup no longer needs to spend substantial upfront capital to build its IT infrastructure. They do not need to update and maintain their servers. They can scale almost instantly.
So today, if a company wants to ramp up its IT infrastructure for the upcoming New Year Sale, it can just rent the necessary computing resources with a click of a few buttons. This is massive. The development teams do not have to worry about if they can get the required computing resources for developing a product feature.
This means faster development, innovation, flexible resources, and greater economies of scale. So now, Netflix can prepare to handle the traffic surge due to the new season of Money Heist without a month.
Cloud computing has been growing rapidly in the last two decades. Many billion-dollar companies have been created due to the ease of acquiring and managing computing resources.
This begs the question of how exactly a Cloud infrastructure works. Let’s look at that briefly.
How does Cloud Work
Let’s start with a simple use case of storage. Most of us would have used Google Drive or iCloud or Dropbox. These are services where we are given some storage space on a remote server. We store our files there and access them using different applications like an Internet browser or an app on our phones. This is a simple example of a Cloud. We no longer need to have huge storage space on our laptops or phones.
In the same manner, many companies now provide other computing resources like processing time or enterprise application usage, for rent. The vendors provide secure ways to connect to their data centres via the Internet (in most cases). The tenants then use these resources as required and release them when it is not required.
The tenants are charged in different ways. For example, some are charged based on the time for which a machine has been on. Others are charged based on how much data was processed or transferred.
Let’s talk about different types of Cloud infrastructure is available for us and how they are different from each other.
Types of Cloud
There are four major types of cloud infrastructures:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Community Cloud
Let’s talk about each of them in some detail.
Public Cloud
A Public Cloud is a model where a third party provides on-demand computing resources over the public Internet. This setup is often shared by multiple organizations and individuals.
These Cloud service providers provide these services in the form of virtual machines or as cloud applications hosted on the Internet. In most cases, the tenants simply rent out the virtual machines and use the computing resources they need.
This is useful when companies need to store some less-sensitive data. The cost of storing and hosting such applications on a Public Cloud is often more cost-effective than using their own data centres.
Another use case is for many B2C companies to handle an unpredictable spike in traffic. The cloud service providers have the ability to quickly cover for the bump in any computing resource requirements.
The other common use case is for creating guest machines for testing and development work. Such Public clouds are often used by development and testing teams to deploy and test their products. This is useful as the servers are mostly in use for a short period of time and renting them instantly is a quicker and more cost-effective process.
Advantages of a public cloud
Large dedicated Cloud service providers will have the ability to invest in the best security resources available. They also attract the most talented engineers to their team. This was very difficult in the old setup.
Public Cloud enables teams to quickly employ computing resources as the need arises. This instant procurement and setup process helps in much faster development cycles and deployment plans. In turn, it spews faster innovation.
With Public Cloud, there is no need for a huge upfront capital investment. The subscriptions cost little to nothing to set up, and you only pay for the resources you use.
There are also huge savings in maintenance and upgrade costs. All of it is managed by the Cloud service provider. Public cloud setups also help in savings in energy costs.
All Cloud Service providers promise a 99.99% uptime. So, these vendors invest a lot in best-in-class infrastructure to ensure 24x7x365 availability of their network and resources.
All public cloud providers have an incentive to optimize their computing resources, to help onboard as many customers as possible. This indirectly also helps the tenants in reducing the wastage of the resources.
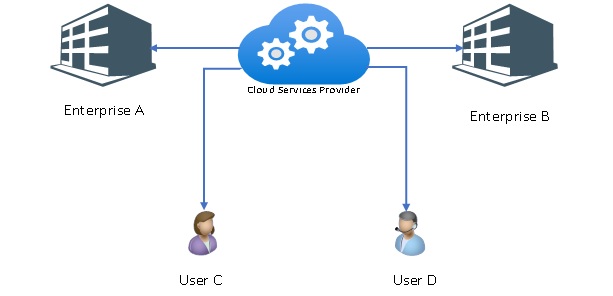
Top public cloud providers
Private CLoud
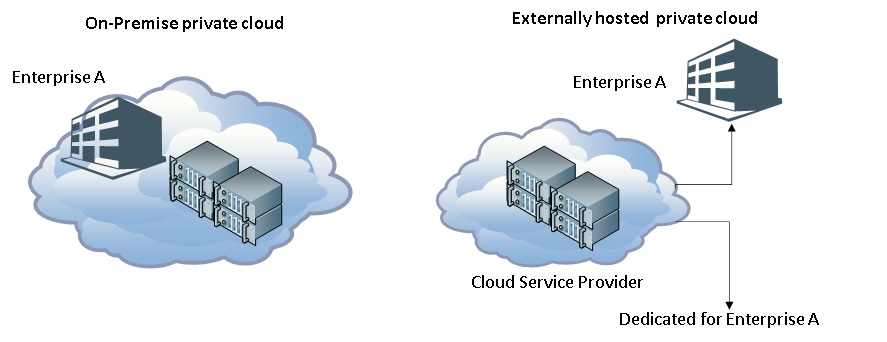
A Private Cloud is one where the entire cloud infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization.
There are two ways this can be done. The Cloud can be hosted in the company’s own data centre, which is called On-premise Private Cloud. It can also be hosted by a cloud service provider at an external location. In that case, the entire data centre will be dedicated to that one tenant. This is called Externally hosted Private Cloud.
In industries where data confidentiality is of prime importance, Hosted Private Cloud is a popular solution. Many Government institutions, Banks and Healthcare companies prefer to use this solution over others. VMware, RedHat and Microsoft are big players in the Private Cloud space.
At its core, both public and private clouds use the same technologies. Both offer computing resources on demand.
Advantages of a hybrid cloud
Many of the internal operations of the companies have predictable computing needs. They do not need the quick scalability and other benefits that a public cloud offers. In a Hybrid cloud model, these predictable operations can be moved to the private cloud thereby optimising the costs for the company.
With Public Cloud, the companies only have a limited set of choices while choosing the computing resources. Some niche organisations often require specialized hardware and software to work efficiently.
A hybrid cloud allows companies to have specialized executions on a private cloud and general processing on a public cloud. This kind of setup optimizes performance and resource usage.
Relying on any one setup has its risks. A public cloud service provider could have outages like the one with AWS in Dec 2021. In the same way, private clouds can also have downtimes for multiple reasons.
A hybrid cloud can help keep the lights up and ensure business continuity for organisations.
Organizations with a hybrid cloud setup can move any core or sensitive data to their private cloud servers and have other applications and services available on the public cloud. This gives them best of both worlds.
The employees will be able to login from anywhere in the world thank to the wide network of public cloud and still be able to access the sensitive data from private cloud stored in a centralized location.
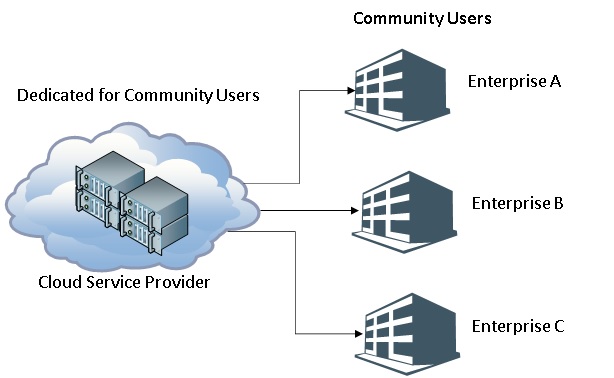
A Community Cloud is a model where the infrastructure is shared between organizations with similar goals and tasks. Many industries have their own specific needs when it comes to an IT infrastructure.
For example, Hospitals have very specific workflows and regulatory requirements. Similarly, Scientific institutions will their own. If a cloud infrastructure is developed that is specifically tuned to the needs of a particular community, it can help in reducing costs and optimizing the resources further for the tenants.
This is a community cloud. The cloud can either be managed by a team in the community or a third-party vendor.
Advantages of a community cloud
Since a community cloud is developed for a set of organizations with similar goals, it helps in providing better security than a public cloud setup while costing less than a private cloud.
Many highly regulated industries find community cloud very effective, as the compliance needs are met together with other companies and thus the companies are less likely to be sued individually. Everyone shares the burden.
Since the infrastructure is shared among all the tenants – the maintenance, upgrades and operational expenses are also shared. This reduces the cost per tenant compared to setting up a private cloud individually.
Conclusion
The above discussion might beg the question – which cloud is best for my business?
There is no one right answer. In fact, the answer would change as an organisation grows and evolves. But a safe and cost-effective way will be to start by moving any insignificant part of your workflow to a Public Cloud.
Using the cloud as a part of your IT workflow requires some training and habit changes but in the long term, it is a step worth taking.
You may like to visit my other blogs on Cloud Computing:
Exploring the Different Types of Cloud Services