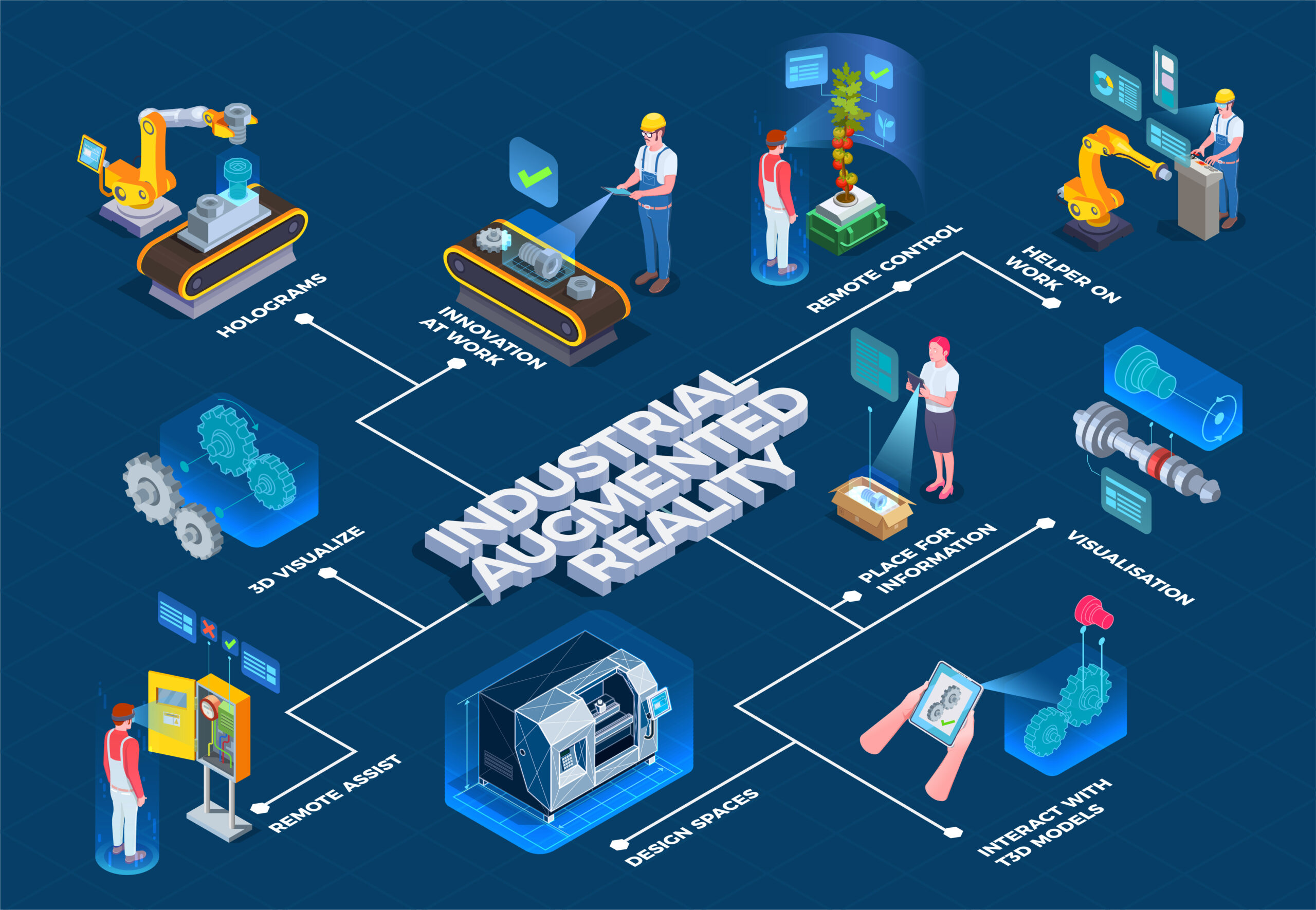
Do you know the estimated market value of the augmented reality sector is $17.6 billion, with a projected increase to $340 billion by 2028?
Augmented reality (AR) is a digitally altered representation of the real world that is made possible through the use of visual, aural, or other sensory aspects. From e-commerce to healthcare, augmented reality (AR) is quickly upending various industries. It offers exciting new opportunities for brand awareness and word-of-mouth marketing.
Have you ever wondered how this innovative technology vastly improves these various sectors?
Below are the top 21 Augmented Reality use cases!
Table of Contents
AR in Education

Augmented reality in education is becoming increasingly popular, as it provides students with a visual and interactive experience which can make learning more engaging and exciting. At this point in civilization, where tablets and computers are now commonplace technologies in schools, teachers and educators now use augmented reality (AR) to enhance students’ learning experiences.
Thanks to AR technologies, students can now examine a 3D hologram from a variety of perspectives. They can more thoroughly examine and comprehend certain concepts by turning or rotating a virtual object in space. Just this alone can completely transform how people learn about things like geometry, anatomy, cosmology, and more.
For example, students studying astronomy may view a detailed map of the solar system, while those studying music may be able to see a musical notation as they practice playing an instrument.
Compared to other approaches, this type of learning increases students’ chances of remembering and understanding what they have learned.
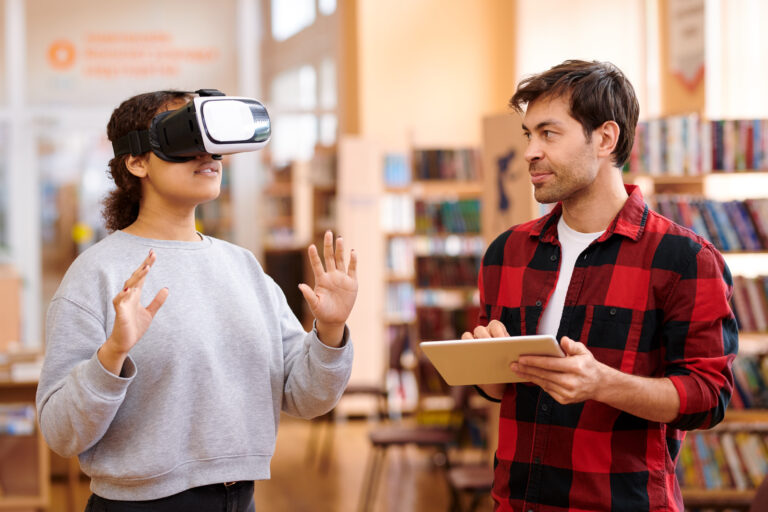
AR in Architecture

Architecture has greatly moved up in stride thanks to AR’s ability to overlap digital images in our physical environment. As a result, architects can use the technology to plan projects and evaluate how they appear in actual environments.
The capacity of AR to provide precise measurements of actual spaces is another significant use of this technology in architecture. One example is the surgical accuracy with which you can measure various physical features using augmented reality equipment like Microsoft’s HoloLens.
AR also provides architects the opportunity to make any essential changes after revising the project on-site. This is significantly faster than any conventional technique and costs much less in terms of materials and manpower.
There are other uses for augmented reality besides visualization. For example, architectural firms often use this technology for effective data management and training
AR in Healthcare
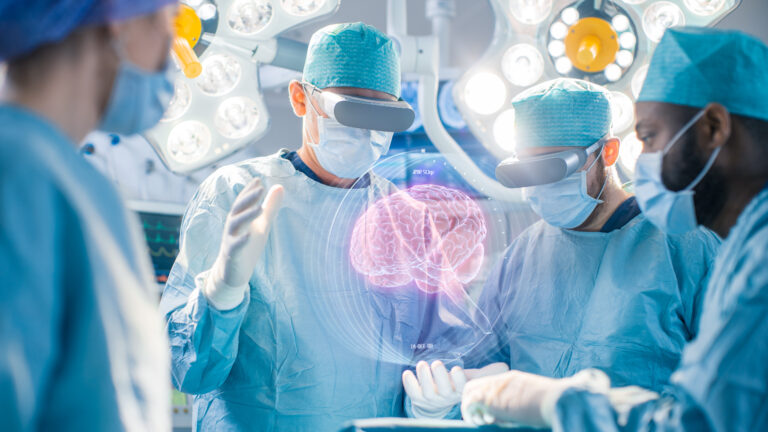
Augmented reality’s effects on healthcare are already being felt. An AR-enabled head-mounted device, for instance, allows a surgeon to monitor patient vitals while performing surgery without having to switch between numerous devices or displays. They are less likely to misinterpret the data or misread it if they do this.
It is anticipated that the current innovative AR developments in healthcare will work like magic to aid medical practitioners in overcoming a number of medical obstacles.
An example is a robotic-assisted surgery, which increases surgical accuracy and dexterity and makes minimally invasive techniques more accessible. The surgeon’s capacity to make better decisions will significantly improve using AR to enhance situational awareness.
Medical professionals facing complex situations can use AR remote assistance software to share a real-time video feed of the situation using a smartphone, tablet, or smart glasses to get require expert guidance.
Traditionally, specialists would need to be physically present to offer their expertise, but AR remote assistance software offers real-time collaboration and guidance, regardless of location.
Doctors can use AR remote assistance technology for remote consultations, guiding patients through self-examinations or certain procedures at home. This proves particularly useful in telemedicine, where patients cannot visit doctors physically.
AR remote assistance can provide surgical assistance.
During complex surgeries, surgeons can receive live guidance from a remote specialist, who can annotate the surgeon’s view to highlight areas of concern or interest. This enhances the precision and safety of operations.
AR in Retail
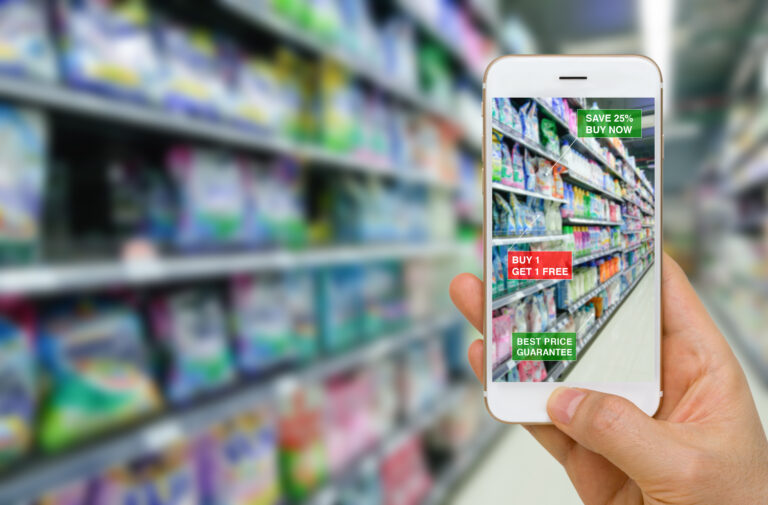

Shopping experiences are quickly being revolutionized by AR in retail! Customers may interact, personalize, and engage with goods and services better with AR in retail, enabling them to make the best buying decisions. Retail AR applications present several opportunities for enterprises to boost consumer satisfaction while cutting costs. Customers may virtually test out merchandise before they buy it, thanks to AR technology. For example, they can see how new appliances will look in their apartment or place of business and how precisely the apparel they want will fit them.
Customers have something to discuss and post on social media thanks to these AR experiences. The ensuing comments and conversations on social media contribute to raising awareness about the product and brand.
Another way AR revolutionizes the retail industry is through the details of the goods that customers opt to test through AR-enhanced shopping. These details reveal a great deal about their tastes, preferences, and purchasing habits and could be used by retailers to create tailored marketing and advertising strategies.
AR in Sports

Large-scale sporting events like the Wimbledon, Olympics, UEFA, and others rely heavily on augmented reality (AR) to creatively deliver exclusive material, event details, and enjoyable interactivity to their audiences. For example, the Major League Baseball Association in the US is investigating the potential for developing AR experiences utilizing metrics from their baseball tracking system. This data can be used to offer AR in a virtual world more accurately and realistically by providing precise information on where athletes and the ball are on the pitch at all times during a match.
Another innovative practice that AR is being used for in sports is utilizing AI, trackers, and computer vision to evaluate the players’ skills at all levels. This drastically alters how athletes exercise and how coaches scout and make choices.
AR in Tourism

Among the most significant sectors of the global economy is tourism. Unfortunately, it was one of the industries most negatively impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but it is now again regaining its expansion and growth.
In order to give tourists more information, traditional and digital travel brochures and maps are being updated with augmented reality content.
Tourists can quickly find useful information by scanning their surroundings using AR. Like getting precise suggestions of free Wi-Fi, restaurant and lodging advice, user reviews, guidance, bus routes, historical events, infographics, personalized itineraries, and many more.
Future advancements in AR are expected to greatly simplify the process of selling trips, vacations, and travel.
AR in Entertainment

With augmented reality, entertainment gains a fresh perspective, and the audience may take an active role in the presentation rather than just being passive consumers. AR adds interaction and interest to the event by fusing the physical world and digital worlds.
Tech movies undoubtedly have a growing fan base in today’s society. They attract tech-savvy individuals of Generations Y and Z. In one way or another, augmented reality technology has been used in some of the most successful blockbuster films ever. For example, in Iron Man, the superhero’s outfit is equipped with potent augmented reality (AR) technologies that offer tons of real-world data so Tony Stark can focus on what he does best. One of the most cutting-edge applications of augmented reality on a head-up display must be this one.
A few illustrations of how AR may make a show memorable include creating exotic worlds, drawing the audience into the story, and offering further details about what is happening on stage.
AR in Gaming

The gaming industry has gained popularity with time, and customer demand for a captivating experience has grown along with it. This experience makes it impossible for users to distinguish between the actual world and the virtual world, which is important to the success of any game in the modern era.
Early adopters of AR technology include the video game industry. On a business level, gaming was the only thing that got people interested in AR. The most well-known AR game so far is Pokémon GO, which became so popular that players flooded the streets to it. Pokémon that had been digitally superimposed on the actual environment. But the options are numerous and always growing. The scope includes traditional board games that have been modified or reproduced entirely with augmented reality and many others.
AR in Navigation

Augmented Reality (AR) is advancing the transportation sector with features including 3D navigation, driving instructions, and topographical images.
AR can be used to navigate between cities. With this technology, you can quickly recognize and travel through locations like stores, galleries, and landscapes. For efficient navigation, AR makes route logistics and visual orienting easier. In addition, augmented reality (AR) applications can spotlight and superimpose directions and guidance points for easy reading of what your camera displays.
Additionally, AR can be used to calculate speed. For example, an augmented reality application may track how fast your car is moving in comparison to other cars and give you recommendations on maneuvers like turns and passes. As a result, performance is increased and driver safety is improved.
AR in Logistics
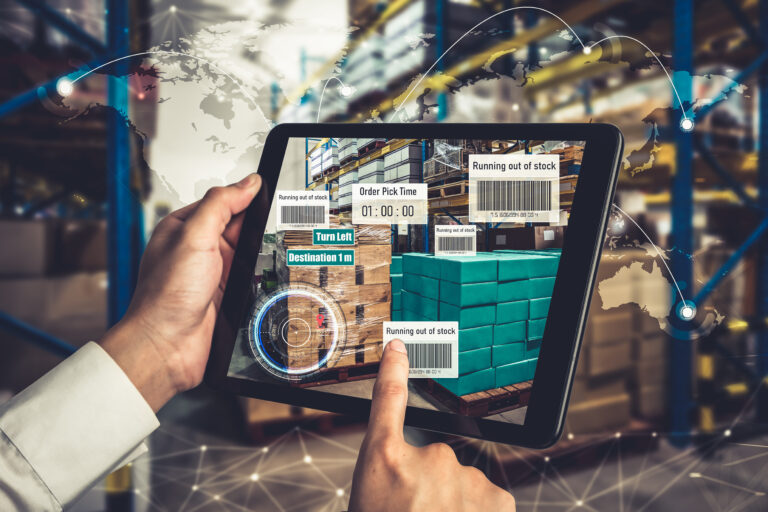

In many logistics sectors, AR offers many chances to improve efficiency and reduce costs. This covers delivery, storage, and route optimization. For example, in cargo loading, loading is accelerated with the use of AR. The written freight lists and load instructions can be efficiently replaced to accomplish this. For instance, it might specify which loader the package should be loaded onto next, the location of the package, or the position it needs to be in the loading cargo or truck.
One of the largest logistics corporations, DHL, has already incorporated smart AR glasses in some of its. These AR glasses show employees the quickest path across a warehouse to find and choose a specific item that needs to be shipped.
AR in virtual dressing room technology
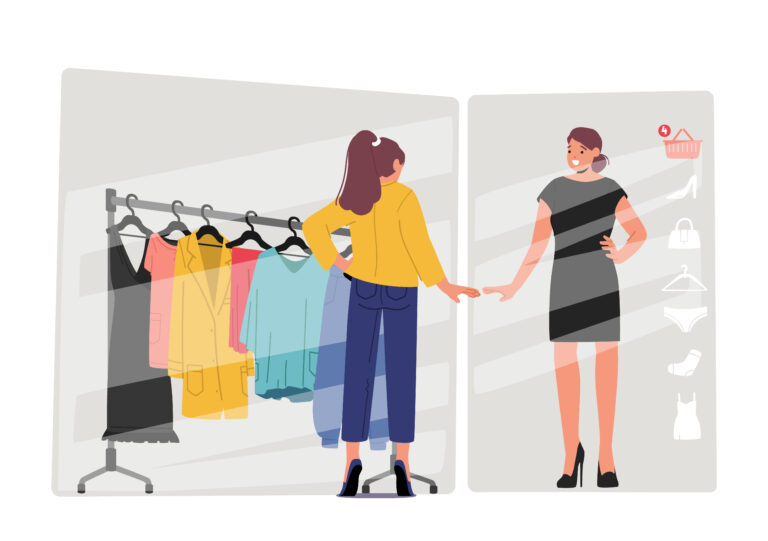

Through the use of augmented reality, buyers may virtually experience in-store purchasing by seeing how an item might appear on them. Customers can, for instance, view how clothing, shoes, jewels, cosmetics, and sunglasses appear on them through virtual representations. This is referred to as “virtual dressing room technology.”
And by 2027, the global market will be expected to reach about $10 billion. The majority of these experiences will be delivered through smart glasses, smartphones, and other portable and wearable technologies.
One other way to utilize AR in fashion is through smart mirrors, which are already a common feature in the storefronts of several prominent retail companies, including Ralph Lauren and H&M.
AR in Security
Industrial surveillance systems currently in use have several limitations. For example, security workers might have access to multi-tiered maps in control centers that show details about the property or the locations of cameras, but not every security guard has access to that data.
The on-the-ground security workers who require such details must rely on their peers in the security control center. As a result, there is a good probability that the proper information will be misconstrued, even if security professionals communicate it correctly.
On-site security staff can now use AR technologies to efficiently communicate their demands in real-time, increasing the security of facilities. They can also receive real-time updates rather than relying on coworkers’ verbal information, allowing them to react more quickly.
AR in Marketing

With the ease of utilizing their smartphones, augmented reality (AR), a new trend in advertising and marketing methods, enables organizations to provide their consumers with one-of-a-kind experiences. AR technology allows advertisers to give apps, as well as other types of content, a personalized touch for the creation of engaging, immersive experiences.
One instance of AR technologies in marketing is when Airwalk leveraged geolocation (an AR feature) to build translucent pop-up stores as part of a campaign to promote its relaunch of the limited-edition Jim shoes Another example is StubHub’s launch of an AR feature for Super Bowl LII that gave ticket buyers access to a virtual 3D representation of the United States Bank Stadium through their mobile app.
AR in Automotive Industry
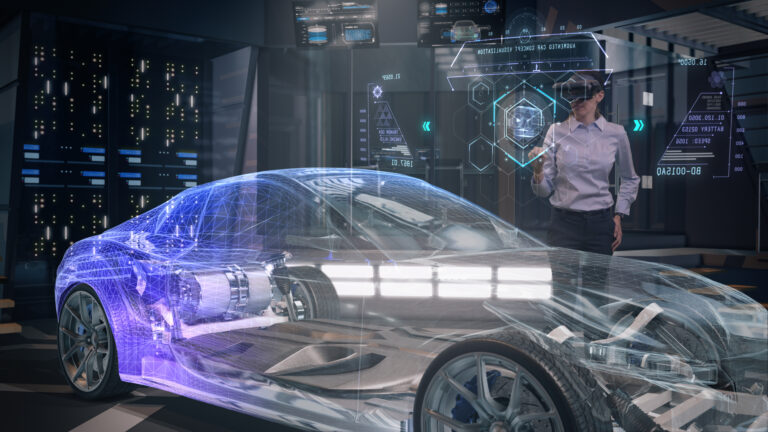

Several auto manufacturers embrace AR experiences quickly in their search for a unique competitive edge. As a result, drivers may receive more information about the environment, the weather, and important events without it impairing their ability to drive, thanks to the usage of projectors on windscreens, see-through displays, and various wearable gear that uses AR.
Drivers can now analyze and interpret information that improves their vision of the road using augmented reality heads-up displays. This kind of display can alert drivers to potential dangers that may be present on the road. Thanks to specially created images that are adapted to the landscape, they can also make navigation simpler than it might be with conventional map software.
Several automakers, including Audi, Volvo, and Nissan, already use this technology.
AR in Home Decor
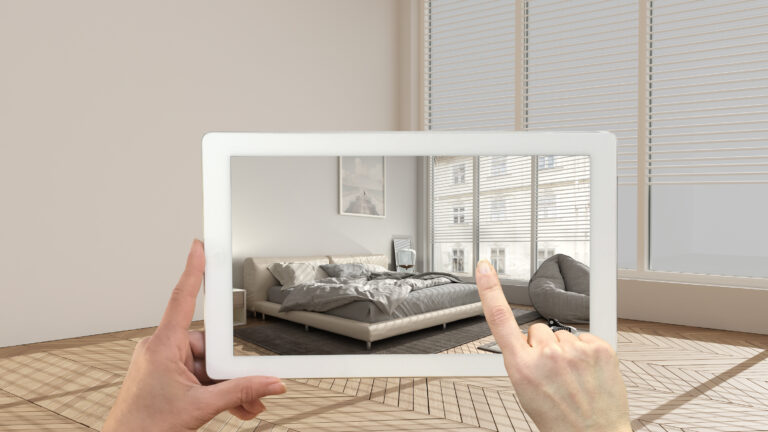

The interior design and architecture industries will benefit most from the highly interactive experience augmented reality technology offers. There is nothing that can equal using 3D models in a real-world setting and assessing them from both the outside and inside. Customers can test their purchases this way, avoiding impulsive purchases altogether and increasing confidence in their purchases.
A popular home decor organization that utilizes AR technology is Home Depot. Users of the Project-Color app from Home Depot can visualize the appearance of a wall color before purchasing the paint. In addition, the software depicts a realistic image when considering shadows, lighting, and other room elements.
AR in Design and Modeling
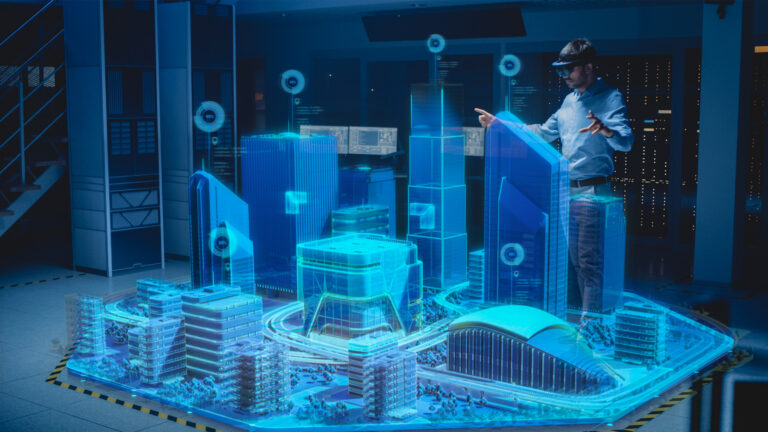

AR assists professionals in visualizing their finalized projects during the creative process in fields including interior design, engineering, and construction. With the aid of headgear, architects, engineers, and design experts may enter their structures immediately to see how they might look and even make adjustments in real-time. Using AR headgear imagery, urban planners could even simulate how complete city plans might appear. AR technology is ideal for any design or modeling task involving geometric distribution.
AR in Appliance and Furniture
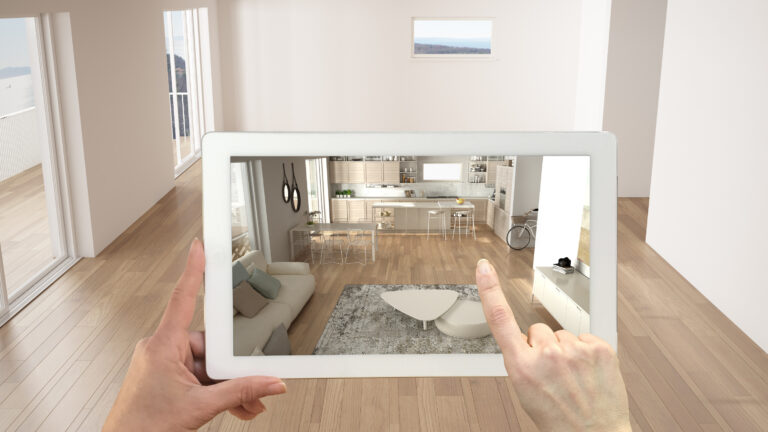

Shoppers can select a product in AR to see it superimposed instantly wherever they position their smartphone. Customers can therefore examine how furniture and equipment appear in their own homes. They may swiftly alter the appliances and furnishings they want to purchase, as well as their colors, sizes, and other characteristics. This is great for imagining how rooms will look and how colors will go together before buying.
Additionally, shoppers can use an immersive 360-degree experience to examine products from any imaginable angle. This helps clients understand the potential worth of a product.
Shopify AR is one solution that allows shoppers to explore products in realistic settings before purchasing them. This is done to ensure that the goods are suitable for their intended use.
AR in Maintenance and Repair
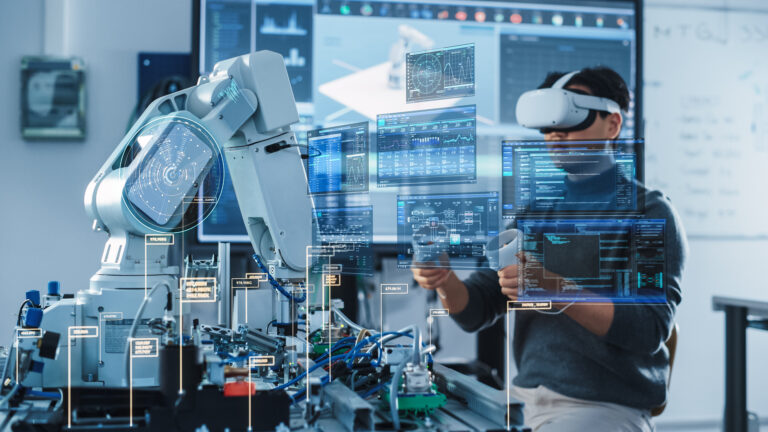

Repair and upkeep of sophisticated equipment are one of AR’s most prevalent industrial uses. Maintenance and repair personnel are starting to employ augmented reality (AR) headgear and lenses while performing their tasks.
AR headgear gives them crucial data on the spot, identifies possible modifications, and points out probable weak spots in a car engine or an MRI device. The strength of this use case will only increase as device IoT technology develops and becomes capable of providing data straight to AR headsets.
AR can direct the specialist through the necessary steps in the desired order for maintenance work. For instance, it might begin with dismantling covers and guards before moving on to replacing filters and inspecting drain valves. In addition, AR is an effective tool for promoting the use of preventative maintenance techniques.
Field Technician can use AR remote assistance software to share a real-time video feed of the situation using a smartphone, tablet, or smart glasses. Through Remote assistance software expert sitting at a remote location can see exactly what the technician sees. The expert can then guide the technician by drawing on the screen, highlighting parts, or overlaying 3D models onto the real-world view. This helps the technician to understand the problem better and perform the necessary actions to resolve the issue.
AR in Vocational Industry
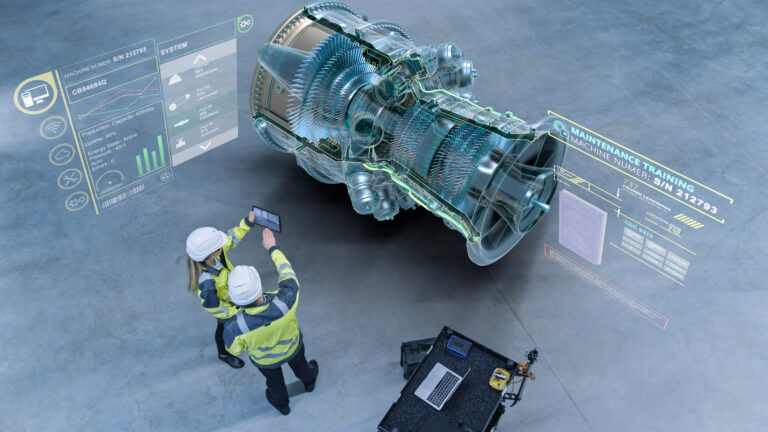

It should be no surprise to see augmented reality making waves in the vocational services sector, given its inventive uses across various industries. Former Gartner Research Vice President Brian Blau notes that there are two key applications for augmented reality in the vocational industry. Firstly, by overlaying detailed schematics and directions over technology in the field, it can serve as an interactive visual assistance for field personnel. Secondly, it can be utilized as a visually oriented virtual tool for clients, offering a “see-what-I-see” method of collaboration with knowledgeable professionals.
Every day, field service professionals are sent to fix a piece of industrial equipment that must be backed up and operating as quickly as possible. It may be a tiny appliance like an air conditioner or a huge one like a wind turbine. These days, specialists can show up on-site equipped with AR lenses or headgear to examine the item they are repairing and rapidly identify and resolve the issue. Additionally, they can work hands-free more quickly than ever before, without needing to leaf through a repair manual.
With the use of AR, vocational workers can also fix consultations and inspections remotely with the same efficiency as if they were there in person.
AR in Training of Medical Students

The use of Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality technology has the potential to improve the scope and efficiency of medical education in a variety of fields, from operating MRI machines to carrying out intricate surgical procedures. For instance, Case Western Reserve University’s Cleveland Clinic students can now study anatomy using AR headsets to explore the human body in an immersive 3D experience.
Students generally learn in a classroom setting for the first few years of medical school. After that, with only a brief surgical rotation real-world experience is gained. Unfortunately, practical surgical training gives such little time. Augmented Reality and Virtual reality training allows medical students to experience surgery up close and personal before their surgical residency. They can witness surgery and even have a first-person view of the operation.
AR in Art
With the use of an WebAR (Web-based Augmented Reality), a QR code, or even the actual painting itself, an artist can provide their audience with an AR experience. The spectator will have a more interesting experience as a result.
For example, it is lovely to view Van Gough’s almond flower. However, imagine being able to observe the flowers around you as they fall under the warm, beautiful sky. The audience becomes more engaged and feels connected to the art through this immersive experience. The artist has the option of adding films, 3D, or images to the corresponding image.
Another AR option for artists is creating AR NFTs. Conventional NFTs merely depict works of art or historical events, whereas AR NFTs incorporate AR signals and components, including the ability to view digital items in your surroundings. In addition, augmented reality technology can be used to explore 3D NFTs. Through websites and applications that support augmented reality, artists can share their immersive AR NFTs experience with others.
Conclusion
Professionals in a variety of industries, such as interior design, engineering, and construction, are using augmented reality to help them visualize their finished products as they go through the design process. AR Headgear allows designers, engineers, and architects to instantly enter their buildings to see how they might appear and even make changes in real-time.
AR innovations are expected to continue to make strides in these industries and many more in the years to come.
